
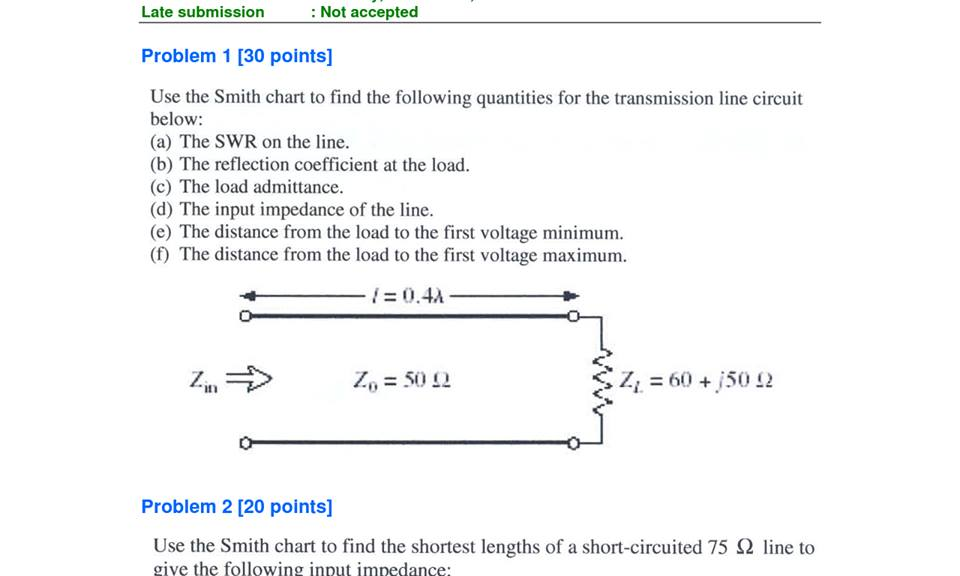
The Smith Chart can be very useful to resolve graphically the transmission line equation, so the input impedance of the transmission line is: Z i n = Z 0 1 + Г e – 2 j β l 1 – Г e ( – 2 j β l, where Г is the reflection coefficient of the transmission line and l is the length of the transmission line.
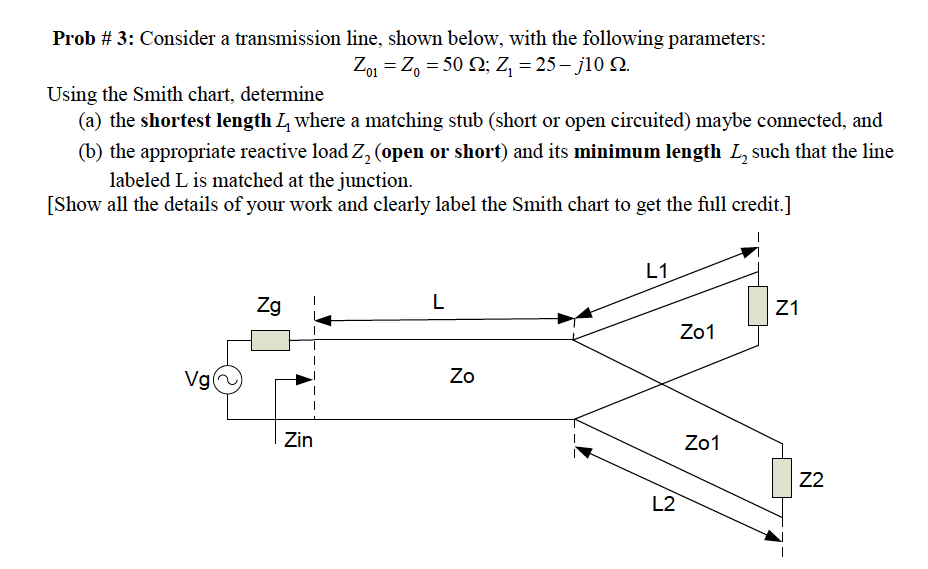
We can see that all the reactance circles lie on the vertical line Г r = 1 , and all the resistance circles lie on the horizontal line Г i = 0. These equations can be rearranged to represent the resistance and reactance circles on the Smith Chart: Г r – r L ( 1 + r L ) 2 + Г i 2 = 1 ( 1 + r L ) 2, ( Г r – 1 ) 2 + ( Г i – 1 x L ) 2 = ( 1 x L ) 2. Resolving the real and imaginary parts of impedance are: r L = 1 – Г r 2 – Г i 2 ( 1 – Г r ) 2 + Г i 2, x L = 2 Г i ( 1 – Г r ) 2 + Г i 2. r L + j x L = 1 + Г r + j Г i 1 – Г r – j Г i. So let’s represent the reflection coefficient and load resistance as complex values: Г = Г r + j Г i, z L = r L + j x L. So the reflection coefficient Г = z L – 1 z L + 1 = | Г | e j θ, here z L = Z L Z 0, or z L = 1 + | Г | e j θ 1 + | Г | e j θ.Īt the beginning of the RF and Microwave course we showed that all the quantities can be represented with their real and imaginary parts. Regarding the impedance, it is better to use normalised quantities z = Z Z 0, where is an impedance, Z 0 is a lossless transmission line impedance.
To do so, impedance or admittance circles should be depicted in the chart. A useful aim of the Smith Chart is that it can convert reflection coefficients to the normal impedances and reverse. And θ is the angle between the reflection coefficient vector and the chart horizontal diameter, -180<θ<180. The reflection coefficient is in the polar form Г = | Г | e j θ, where | Г | is the reflection coefficient magnitude radius from the plot centre. The Smith Chart is based on the polar system of the voltage reflection coefficient Г. Smith, and despite of being developed so long ago, it is still in use and is the most famous and helpful tool among engineers. It is a very useful tool for solving the problems of RF engineers with regards to transmission lines.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
